Genes, transcripts and genomic regions in Ensembl Plants, Demo
The front page of Ensembl Plants is found at plants.ensembl.org. It contains lots of information and links to help you navigate Ensembl Plants:
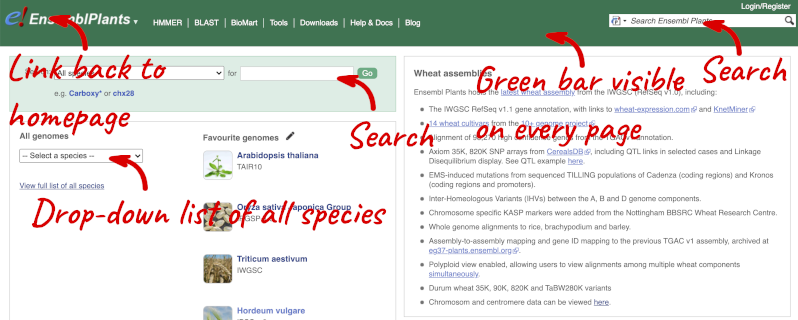
At the top left you can see the current release number and what has come out in this release.
Click on View full list of all species.
Click on the common name of your species of interest to go to the species homepage. We’ll click on Triticum aestivum.
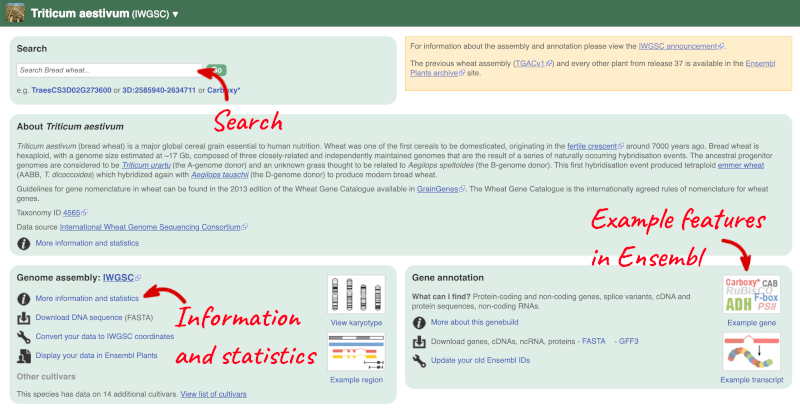
Here you can see links to example pages and to download flatfiles. To find out more about the genome assembly and genebuild, click on More information and statistics.
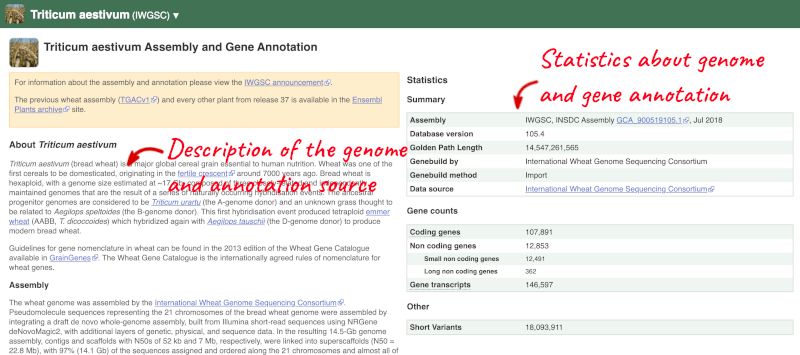
Here you’ll find a detailed description of how to the genome was produced and links to the original source. You will also see details of how the genes were annotated.
We’re going to look at the wheat TraesCS3D02G273600 gene. From plants.ensembl.org or the wheat species homepage, type _ TraesCS3D02G273600_ into the search bar and click the Go button.
The gene tab
Click on TraesCS3D02G273600 from the search hits. The Gene tab should open:
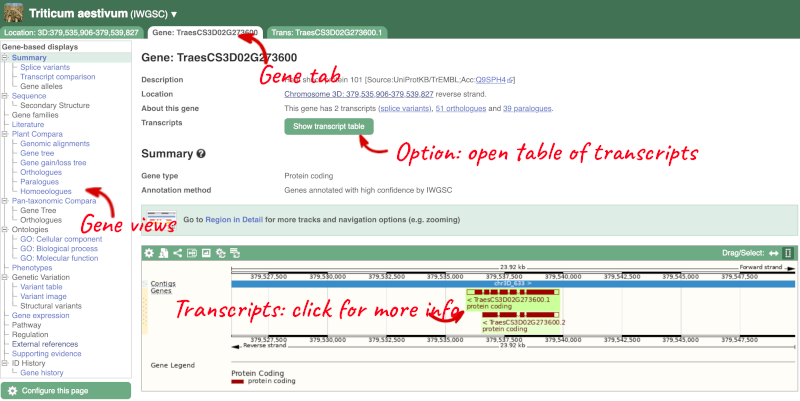
This page summarises the gene, including its location, name and equivalents in other databases. At the bottom of the page, a graphic shows a region view with the transcripts. We can see exons shown as blocks with introns as lines linking them together. Coding exons are filled, whereas non-coding exons are empty. We can also see the overlapping and neighbouring genes and other genomic features.
There are different tabs for different types of features, such as genes, transcripts or variants. These appear side-by-side across the blue bar, allowing you to jump back and forth between features of interest. Each tab has its own navigation column down the left hand side of the page, listing all the things you can see for this feature.
Let’s walk through this menu for the gene tab. How can we view the genomic sequence? Click Sequence at the left of the page.
The sequence is shown in FASTA format. The FASTA header contains the genome assembly, chromosome, coordinates and strand (1 or -1) – this gene is on the positive strand.
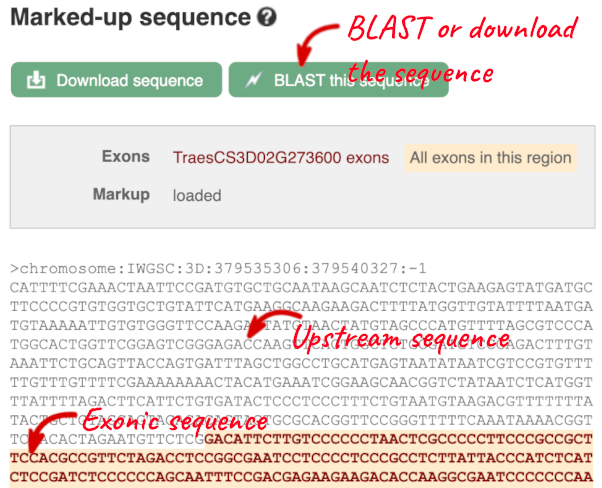
Exons are highlighted within the genomic sequence, both exons of our gene of interest and any neighbouring or overlapping gene. By default, 600 bases are shown up and downstream of the gene. We can make changes to how this sequence appears with the blue Configure this page button found at the left. This allows us to change the flanking regions, add variants, add line numbering and more. Click on it now.
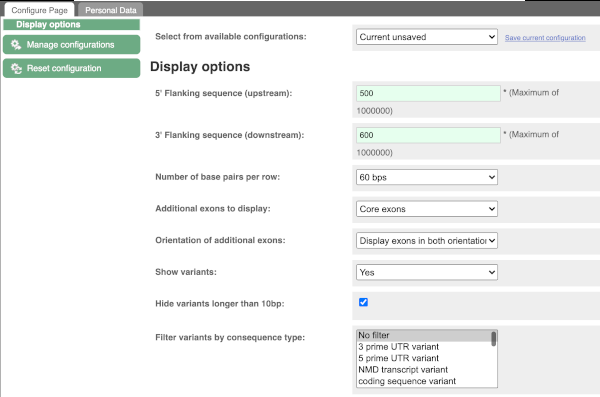
Once you have selected changes (in this example, Show variants and Line numbering) click at the top right.

You can download this sequence by clicking in the Download sequence button above the sequence:

This will open a dialogue box that allows you to pick between plain FASTA sequence, or sequence in RTF, which includes all the coloured annotations and can be opened in a word processor. If you want run a sequence analysis tool, download as FASTA sequence, whereas if you want to analyse the sequence visually, RTF is best for this. This button is available for all sequence views.
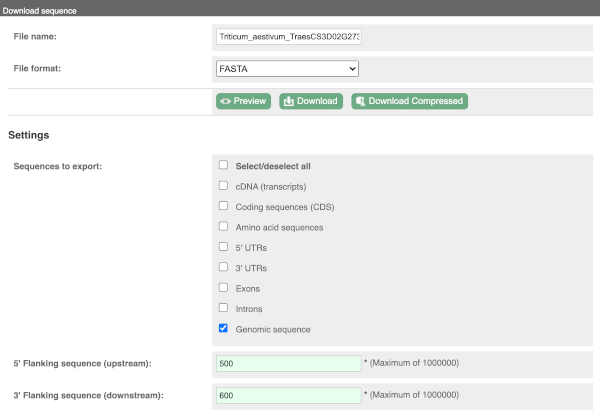
To find out what the protein does, have a look at GO terms from the Gene Ontology consortium. There are three pages of GO terms, representing the three divisions in GO: Biological process (what the protein does), Cellular component (where the protein is) and Molecular function (how it does it). Click on GO: Biological process to see an example of the GO pages.
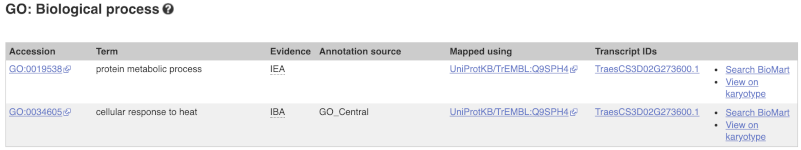
Here you can see the functions that have been associated with the gene. There are three-letter codes that indicate how the association was made, as well as links to the specific transcript they are linked to.
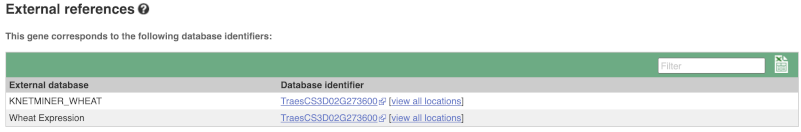
We also have links out to other databases which have information about our genes and may focus on other topics that we don’t cover, like Gene Expression Atlas or OMIM. Go up the left-hand menu to External references:
Demo: The transcript tab
We’re now going to explore the different transcripts of TraesCS3D02G273600. Click on Show transcript table at the top.

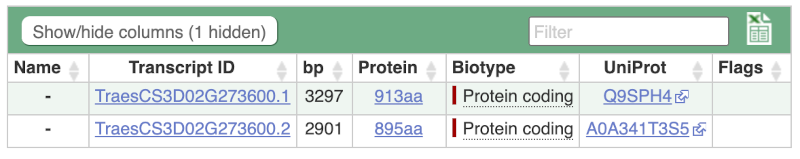
Here we can see a list of all the transcripts of TraesCS3D02G273600 with their identifiers, lengths and biotypes. Click on the ID of the largest transcript, HORVU5Hr1G100140.2.
You are now in the Transcript tab for TraesCS3D02G273600.1. We can still see the gene tab so we can easily jump back. The left hand navigation column provides several options for the transcript TraesCS3D02G273600.1 - many of these are similar to the options you see in the gene tab, but not all of them. If you can’t find the thing you’re looking for, often the solution is to switch tabs.
Click on the Exons link. This page is useful for designing RT-PCR primers because you can see the sequences of the different exons and their lengths.
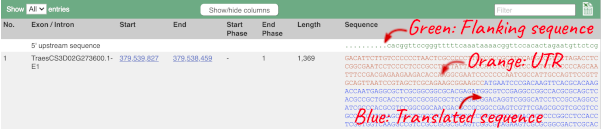
You may want to change the display (for example, to show more flanking sequence, or to show full introns). In order to do so click on Configure this page and change the display options accordingly.
Now click on the cDNA link to see the spliced transcript sequence with the amino acid sequence. This page is useful for mapping between the RNA and protein sequences, particularly genetic variants.
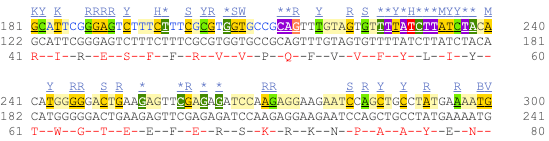
UnTranslated Regions (UTRs) are highlighted in dark yellow, codons are highlighted in light yellow, and exon sequence is shown in black or blue letters to show exon divides. Sequence variants are represented by highlighted nucleotides and clickable IUPAC codes are above the sequence.
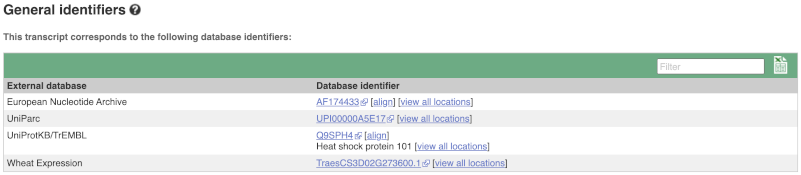
Next, follow the General identifiers link at the left. Just like the External References page in the gene tab, this page shows links out to other databases such as RefSeq, UniProtKB, PDBe and others, this time linked to the transcript or protein product, rather than the gene.
If you’re interested in protein domains, you could click on Protein summary to view domains from Pfam, PROSITE, Superfamily, InterPro, and more. These are all plotted against the transcript sequence, with the exons shown in alternating shades of purple at the top of the page. Alternatively, you can go to Domains & features to see a table of the same information.

Demo: The location tab
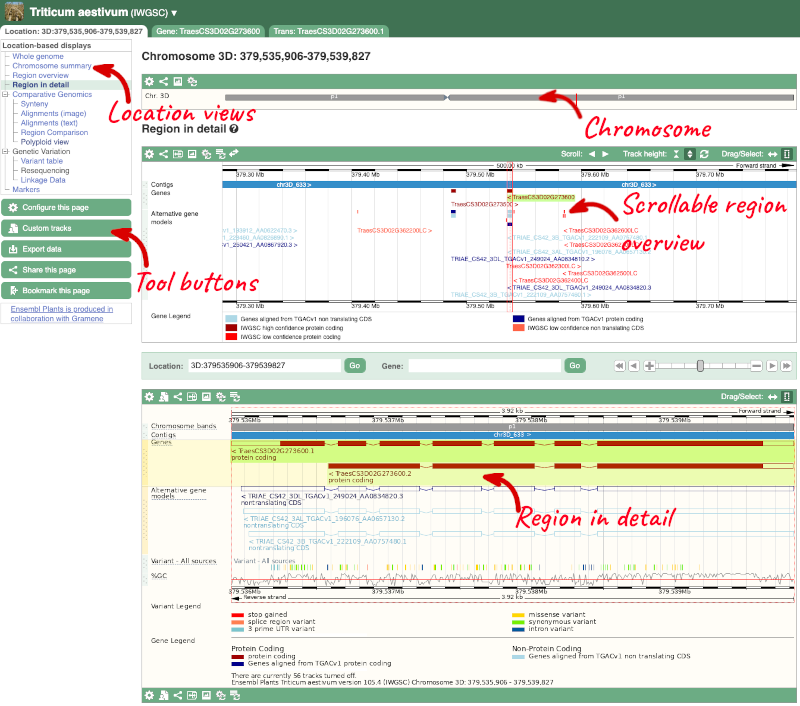
Click on the Location tab to view the Region in Detail page, which displays the genes and other related data aligned against the reference genome.
Click on the  button to view page-specific help. The help pages provide text, labelled images and, in some cases, help videos to describe what you can see on the page and how to interact with it.
button to view page-specific help. The help pages provide text, labelled images and, in some cases, help videos to describe what you can see on the page and how to interact with it.
The Region in detail page is made up of three images, let’s look at each one in detail.
1) The first image shows the chromosome:

The region we’re looking at is highlighted on the chromosome.
2) The second image shows a 500kb region around our selected region. This view allows you to scroll back and forth along the chromosome.
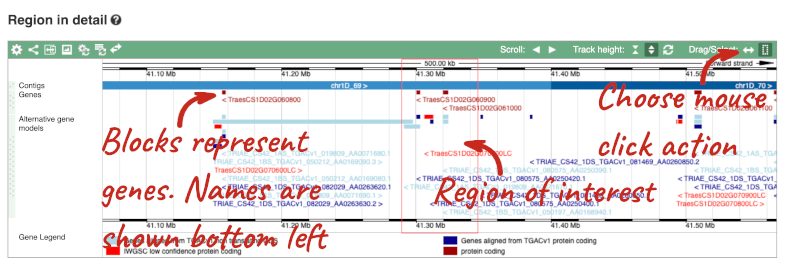
Click on the Drag/Select button  to change the action of your mouse click. Now you can scroll along the chromosome by clicking and dragging within the image. As you do this you’ll see the image below grey out and two blue buttons appear. Clicking on Update this image would jump the lower image to the region central to the scrollable image. We want to go back to where we started, so we’ll click on Reset scrollable image.
to change the action of your mouse click. Now you can scroll along the chromosome by clicking and dragging within the image. As you do this you’ll see the image below grey out and two blue buttons appear. Clicking on Update this image would jump the lower image to the region central to the scrollable image. We want to go back to where we started, so we’ll click on Reset scrollable image.

3) The third image is a detailed, configurable view of the region.
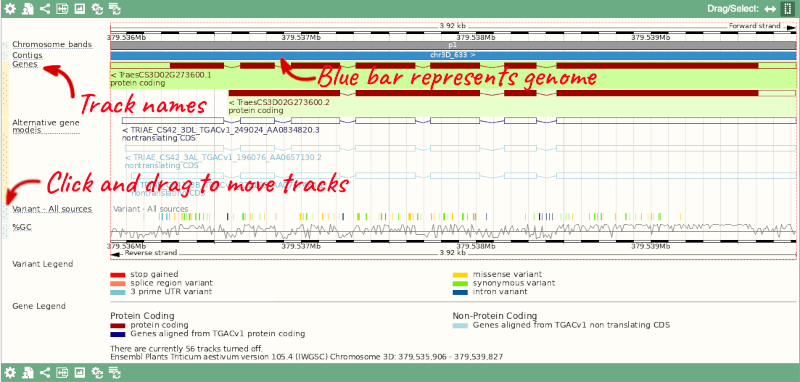
Here you can see various tracks, which is what we call a data type that you can plot against the genome. Some tracks, such as the transcripts, can be on the forward or reverse strand. Forward stranded features are shown above the blue contig track that runs across the middle of the image, with reverse stranded features below the contig. Other tracks, such as variants, regulatory features or conserved regions, refer to both strands of the genome, and these are shown by default at the very top or very bottom of the view.
You can use click and drag to either navigate around the region or highlight regions of interest, Click on the Drag/Select option at the top or bottom right to switch mouse action. On Drag, you can click and drag left or right to move along the genome, the page will reload when you drop the mouse button. On Select you can drag out a box to highlight or zoom in on a region of interest.
With the tool set to Select, drag out a box around an exon and choose Mark region.
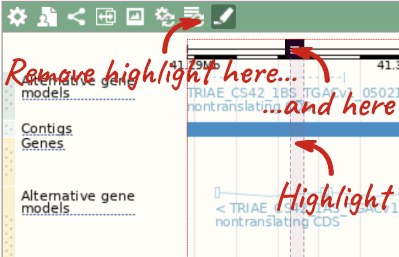
The highlight will remain in place if you zoom in and out or move around the region. This allows you to keep track of regions or features of interest.
We can edit what we see on this page by clicking on the blue Configure this page menu at the left.

This will open a menu that allows you to change the image.
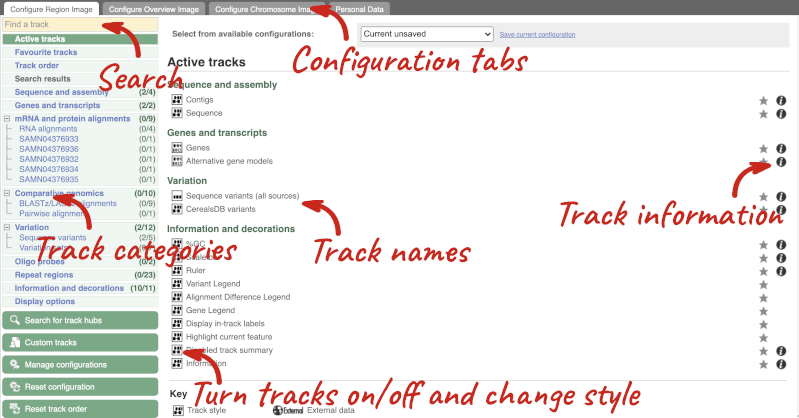
When you launch the view, you will see the tracks that are currently turned on with their names on the left and an info icon on the right, which you can click on to expand the description of the track. Turn them on or off, or change the track style by clicking on the box next to the name. More details about the different track styles are in this FAQ: http://www.ensembl.org/Help/Faq?id=335.
You can find more tracks to add by either exploring the categories on the left, or using the Find a track option at the top left. Type in a word or phrase to find tracks with it in the track name or description.
Let’s add some tracks to this image. Add:
- EMS-induced mutation variants
- Type I Transposons/LINE (Repeats: Repbase)
Now click on the tick in the top left hand to save and close the menu. Alternatively, click anywhere outside of the menu. We can now see the tracks in the image.
If the track is not giving you can information you need, you can easily change the way the tracks appear by hovering over the track name then the cog wheel to open a menu. To make it easier to compare information between tracks, such as spotting overlaps, you can move tracks around by clicking and dragging on the bar to the left of the track name.

Due to hybridisations in wheat’s evolutionary history, it has a hexaploid genome with related homoeologous regions. We can compare these with the Polyploid view. Click on the Polyploid view link in the left-hand menu.
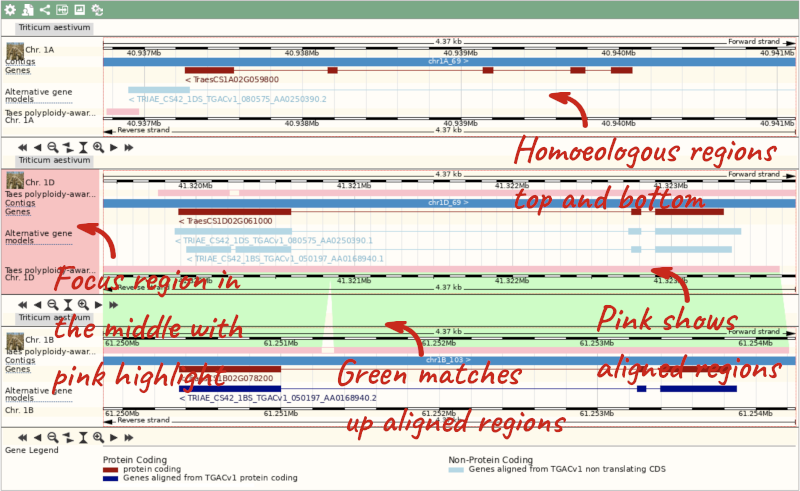
This view also allows us to configure the page, as we could with the main region view, so that we can compare other features between the homoeologous chromosomes.