Filter Events by Year
Ensembl Browser & VEP Workshop - Summer School in Bioinformatics
Course Details
- Lead Trainer
- Louisse Paola Mirabueno
- Event Date
- 2023-06-15
- Location
- Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, UK
- Description
- Work with the Ensembl Outreach team to get hands-on experience accessing and analysing variation data with the Ensembl genome browser.
Demos and exercises
VEP
We have identified 10 variants on human chromosome eight in a patient with neurodegenerative symptoms including dystonia.
We will use the Ensembl VEP to determine:
- Have my variants already been annotated in Ensembl?
- What genes are affected by my variants?
- Do any of my variants affect gene regulation?
Go to the front page of Ensembl and click on the Variant Effect Predictor.

This page contains information about the VEP, including links to download the script version of the tool. Click on Launch VEP to open the input form:
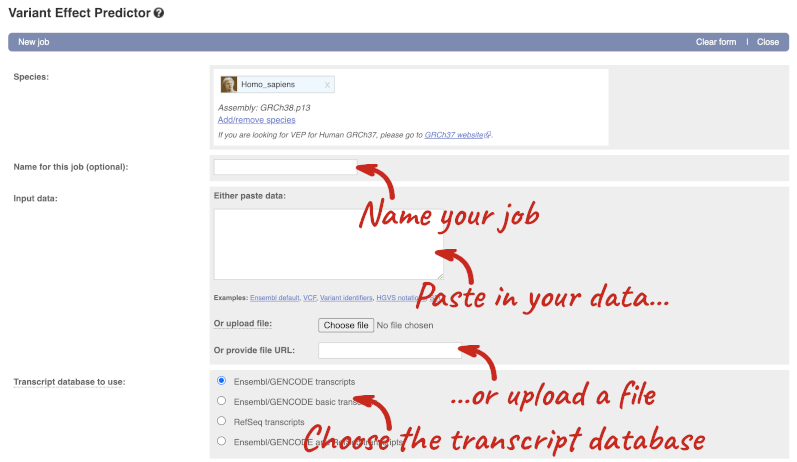
The data is in VCF format:
chromosome coordinate id reference alternative
Put the following into the Paste data box:
8 22410000 var1 G A
8 22412087 var2 C G
8 22408305 var3 T C
8 22409953 var4 C T
8 22414115 var5 C T
8 22406904 var6 GA C
8 22366942 var7 G A
8 22408348 var8 C T
8 22404716 var9 GCTGCTGCTGCTGC GCTGCTGC
8 22404808 var10 T C
The VEP will automatically detect that the data is in VCF.
There are further options that you can choose for your output. These are categorised as Identifiers, Variants and frequency data, Additional annotations, Predictions, Filtering options and Advanced options. Let’s open all the menus and take a look.

Hover over the options to see definitions.
We’re going to select some options:
- HGVS, annotation of variants in terms of the transcripts and proteins they affect, commonly-used by the clinical community
- gnomAD (exomes) allele frequencies
- Protein matches
- Phenotypes
When you have selected everything you need, scroll right to the bottom and click Run.

The display will show you the status of your job. It will say Queued, then automatically switch to Done when the job is done, you do not need to refresh the page. You can edit or discard your job at this time. If you have submitted multiple jobs, they will all appear here.
Click View results once your job is done.
In your results you will see a graphical summary of your data, as well as a table of your results.
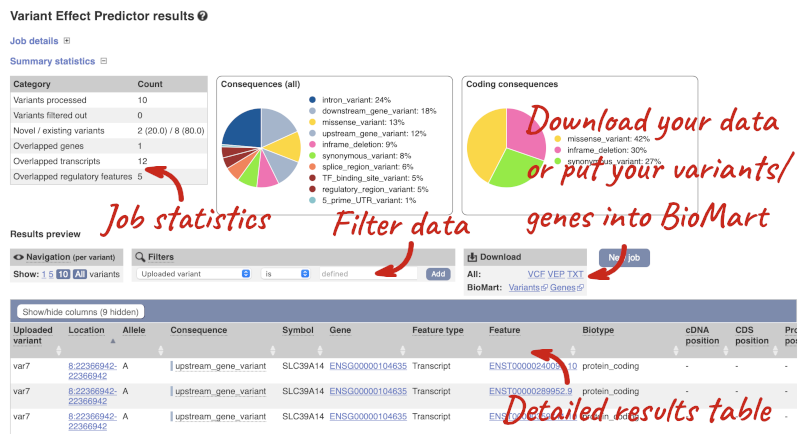
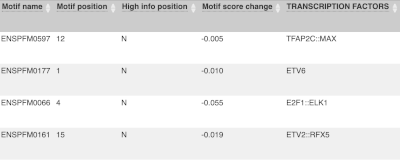
The results table is enormous and detailed, so we’re going to go through it by section. The first column is Uploaded variant. If your input data contains IDs, like ours does, the ID is listed here. If your input data is only loci, this column will contain the locus and alleles of the variant. You will notice that the variants are not neccessarily in the order they were in your input. You will also see that there are multiple lines in the table for each variant, with each line representing one transcript or other feature the variant affects.
You can mouse-over any column name to get a definition of what is shown.
The next few columns give the information about the feature the variant affects, including the consequence. Where the feature is a transcript, you will see the gene symbol and stable ID and the transcript stable ID and biotype. Where the feature is a regulatory feature, you will get the stable ID and type. For a transcription factor binding motif (labelled as a Motif name) you will see just the ID. Most of the IDs are links to take you to the gene, transcript or regulatory feature homepage.
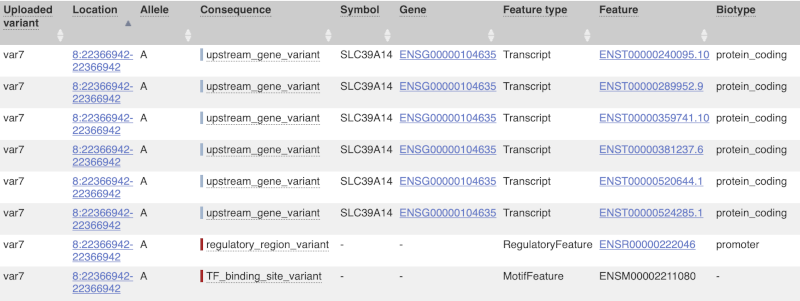
This is followed by details on the effects on transcripts, including the position of the variant in terms of the exon number, cDNA, CDS and protein, the amino acid and codon change, transcript flags, such as MANE, on the transcript, which can be used to choose a single transcript for variant reporting, and pathogenicity scores. The pathogenicity scores are shown as numbers with coloured highlights to indicate the prediction, and you can mouse-over the scores to get the prediction in words. Two options that we selected in the input form are the HGVS notation, which is shown to the left of the image below and can be used for reporting, and the Protein matches to the right. The Protein matches list the proteins domains found, and where available, provide a link to the 3D protein model which will launch a LiteMol viewer, highlighting the variant position.
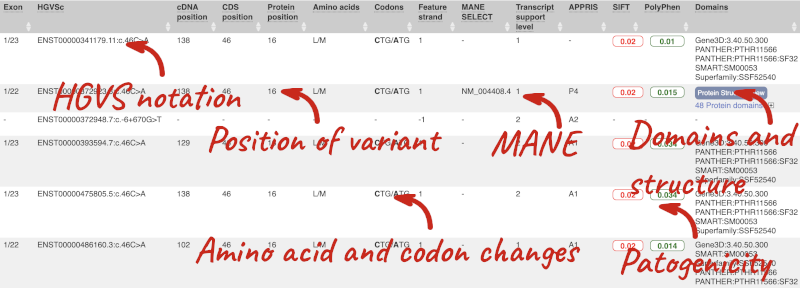
Where the variant is known, the ID of the existing variant is listed, with a link out to the variant homepage. In this example, IDs from dbSNP and COSMIC are shown, but sometimes you will see IDs from other sources as well. The VEP also looks up the variant in the Ensembl database and pulls back the allele frequency (AF in the table), which will give you the 1000 Genomes Global Allele Frequency and allele frequencies from gnomAD. We can also see ClinVar clinical significance and the phenotypes associated with known variants or with the genes affected by the variants, with the variant ID listed for variant associations and the gene ID listed for gene associations, along with the source of the association.
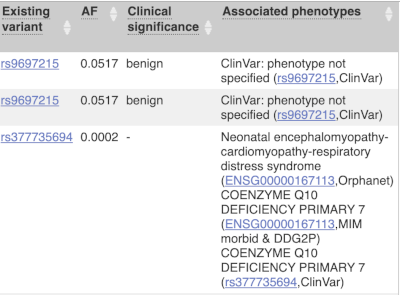
For variants that affect transcription factor binding motifs, there are columns that show the effect on motifs (you may need to click on Show/hide columns at the top left of the table to display these). Here you can see the position of the variant in the motif, if the change increases or decreases the binding affinity of the motif and the transcription factors that bind the motif.
Let’s sort the table by Impact using the little upward triangle next to the column name (you may need to click on Show/hide columns to find it).
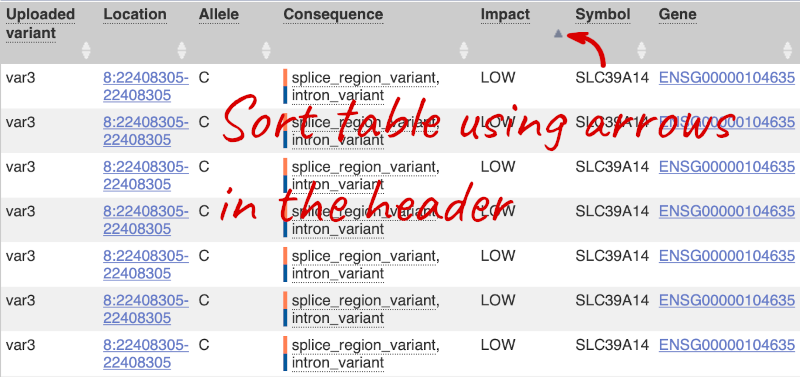
Impact is a subjective classification of the severity of the variant consequence, based on agreement with other variant annotators. It groups variant consequences into four categories: high, moderate, low and modifier. There is no high impact variant on our list, but we have some moderate variant classes such as missense or inframe deletion. Let’s filter the table to get rid of low impact variants now.
Above the table is the Filter option, which allows you to filter by any column in the table. You can select a column from the drop-down, then a logic option from the next drop-down, then type in your filter in the following box. We will try a filter of Impact, followed by is then moderate, which will give us only variant consequences, which might change protein effectiveness. You’ll notice that as you type moderate, the VEP will make suggestions for an autocomplete.
We are still left with quite a few variants. As we are dealing with a rare disorder, we can filter them by the allele frequency assuming that varaints causal of rare diseases should be very rare in the population. Choose gnomADe AF as the filter now, followed by < then 0.005, which will leave us with rare variants found below 0.5% frequency in the general population.
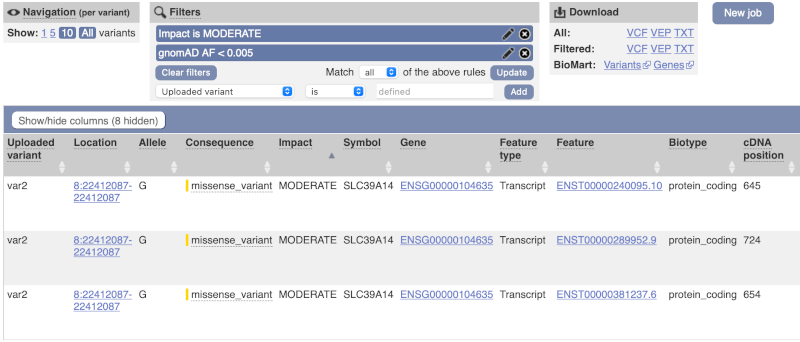
Only one variant meets our criteria. It is a benign missense variant reported on three different transcripts of the SLC39A14 gene, including the MANE Select transcript (NM_001128431.4). Note that the allele frequency for some rare or novel variants might be unknown. Let’s take that into account by editing our allele frequency filter. Change the gnomADe AF filter to is not then defined (leave the text box empty to set it to default defined).
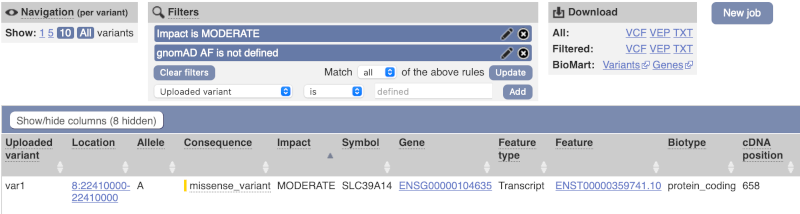
We are left with one pathogenic missense variant of unknown frequency reported on the MANE Plus clinical transcript (NM_015359.6) and associated with hypermagnesemia with dystonia, which can potentially explain our clinical case.
You can export your VEP results in various formats, including VCF. When you export as VCF, you will get all the VEP annotation listed under CSQ in the INFO column. After filtering your data, you will see that you have the option to export only the filtered data. You can also drop all the genes you have found into the Gene BioMart, or all the known variants into the Variation BioMart to export further information about them.